Scientists and doctors alarming (not only in the U.S.), because an increasing proportion of people worldwide are overweight. Meanwhile, progress means that not only people gain weight, but also websites. This is influenced by many reasons, including too many javascript libraries used in popular CMS.
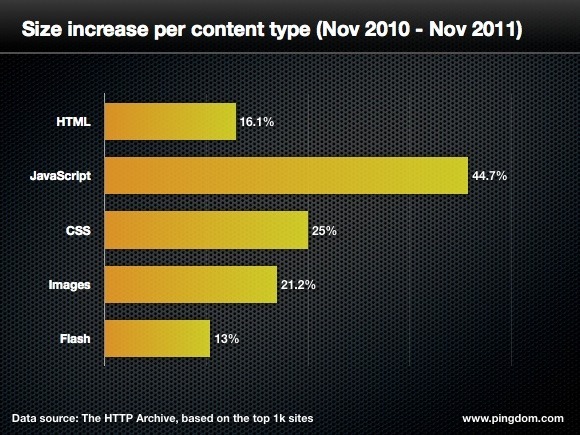
BBC informs that, the average web page is now about 965 kilobytes in size, reveals a study of top sites by the HTTP Archive. The figure is 33% up on the same period in 2010 when the average webpage was a svelte 726 kilobytes. By the way, back in 1995, the average web page was over ~15 KB. The 33 percent jump is due in large part to more images and third-party scripts like ads and analytics. Javascript content, spurred on by the rise of HTML5, has grown over the last year by 44.7 percent, according to analysis by Royal Pingdom. Keeping webpages small is likely to become more important as increasing numbers of people browse the web on the move.
“Big pages generally take longer to load, which can mean visitors quit if a page takes too long to appear.”
Unfortunately, optimization of the parties often do not go hand in hand with the expectations of users of desktop browsers and devices connected to broadband. On the desktop we require high-resolution graphics, interactive elements, animation and multimedia materials. Of course, pages can be optimized in many ways: you can compress CSS, JavaScript recompile, appropriately selected graphic file formats and so on. You can also take advantage of services like Amazon S3, Cloudflare, but there are certain limits not to jump. Unfortunately, the greater are the requirements for the sides of fountains, the less chance that they will load quickly on mobile connections.
Fortunately, a lot of sites already use mobile browsers identifying (some template frameworks have this option build-in) and possibility of serving them a “lighter” version of sites, and technologies to optimize the page before sending it to the device, as used by Opera Mini, Amazon Silk or Opera Turbo technology.
Blame advertisers, if they provide to you “heavy weight” of advertising (eg. flash). For them, the most important is the effect of “wow”, but strongly slow down web pages, which in effect forces users to block ads using tools like Adblock.